According to a report from the Japan Broadcasting Association (NHK) on the 24th, relevant personnel revealed that the Japanese government and Tokyo Electric Power Company have basically finalized that in the future, through the construction of an undersea tunnel, the sewage from the Fukushima nuclear power plant will be drained into the sea near 1 km from the coast.
Nuclear sewage diffusion simulation
After the discharge, a large number of marine organisms will be the first to be harmed. The tritium and carbon-14 in nuclear waste water are easily absorbed by algae and plankton, and gradually accumulate along the food chain. In the end, a large amount of radioactive material stays in the big fish at the top of the food chain and is brought to the table by people.

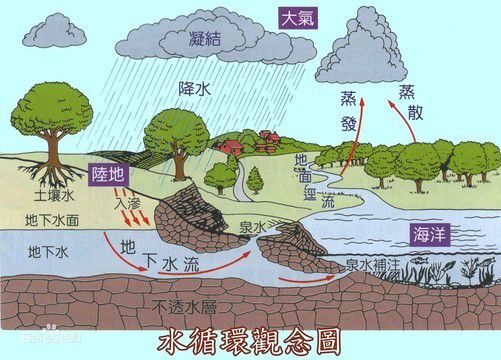
Then some people will say, can I not eat fish? Even if you don't eat fish, the tritium in nuclear wastewater will also enter the cloud with the water cycle, and then enter the reservoir or groundwater system through rain. It will also be absorbed by people drinking. So protecting the health of drinking water is very important!
What is reverse osmosis? Do you still remember the osmosis learned in high school biology compulsory 1? The two conditions for osmosis are to have a semi-permeable membrane and to have a concentration difference. Under the action of osmosis, water molecules in a low-concentration solution will flow through the semi-permeable membrane to a high-concentration liquid. To ensure the concentration balance.

On the contrary, reverse osmosis is the opposite. When pressure is applied to a high-concentration solution, water molecules in the solution will flow through the semi-permeable membrane to the low-concentration area, and the salt in the solution cannot pass through the semi-permeable membrane to achieve the water filtration effect.
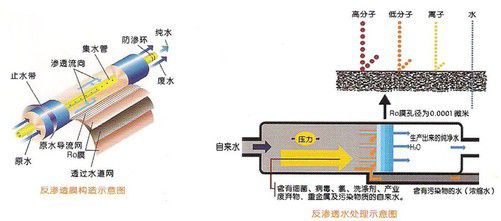
Now back to the original question: Can the reverse osmosis filter water purifier, which can filter even urine into drinking water, purify nuclear waste water? The answer is that it can be filtered, but not completely. There are indeed physicists doing research in this direction.


Based on the results, radioactive isotopes with larger molecular weights such as iodine, ruthenium, rhodium, tellurium, cobalt, and strontium in nuclear wastewater can indeed be partially intercepted by the RO reverse osmosis membrane. But the hydrogen isotope tritium, the super heavy water formed after combining with oxygen can easily pass through the RO membrane. Moreover, most of the radioisotopes are corrosive, and the maintenance and disposal of the filter element is also very cumbersome. Therefore, the use of RO reverse osmosis filtration and purification of nuclear wastewater still needs more experiments and technical support of new materials.
Of course, the domestic water dispenser has to be used where it should be used. Although the water produced by the water plant meets drinking standards, due to aging and rusty pipelines, pollution of the secondary water supply in the community, etc., the tap water will not be so safe after it reaches your home. If you feel that the tap water from your home has a peculiar smell or even the color is wrong, then hurry up and buy an RO reverse osmosis water purifier for yourself!






 How to choose a filtered water purifier: help you buy the best water purifier! Keep your water as pure as it can be!
How to choose a filtered water purifier: help you buy the best water purifier! Keep your water as pure as it can be!
 Analysis and solutions to the causes of reverse osmosis membrane fouling
Analysis and solutions to the causes of reverse osmosis membrane fouling
 Do you know how to extend the life of your reverse osmosis membrane?
Do you know how to extend the life of your reverse osmosis membrane?
 How much do you know about ultrafiltration technology and ultrafiltration membranes?? Ultrafiltration Knowledge Points Collection, you deserve it!
How much do you know about ultrafiltration technology and ultrafiltration membranes?? Ultrafiltration Knowledge Points Collection, you deserve it!